Is Okra Water Actually Healthy? What Experts Think of the New TikTok Trend

- TikTok’s new okra water health trend claims to help with blood sugar, gut health, and weight.
- Nutrition experts say the vegetable itself is chock-full of healthy nutrients.
- However, the health claims for okra water may be exaggerated.
You’re likely familiar with okra. The edible seed pods of the okra plant are used in a variety of dishes, including fried okra, okra chips, and gumbo.
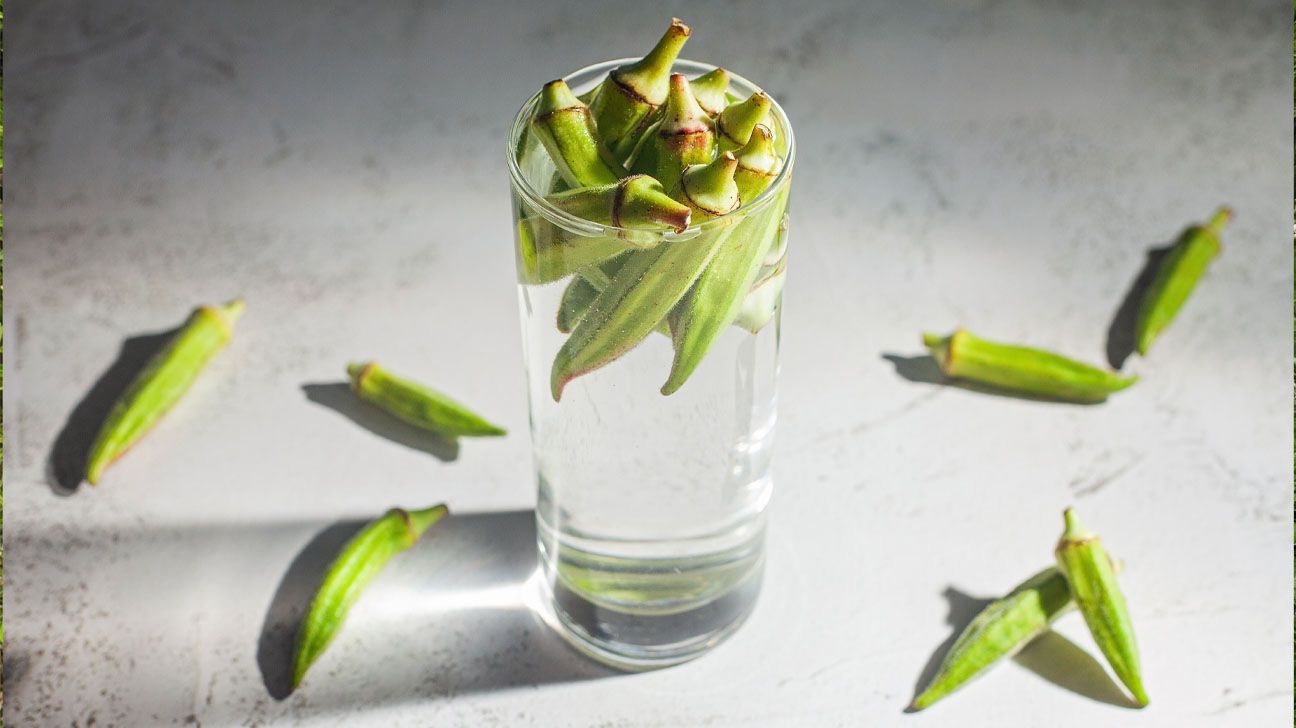
Now, however, TikTok has come up with a new use for the vegetable: okra water.
“The trend involves soaking raw okra pods in water overnight, then drinking the infused water the next day,’ Angela Graham, MBA, RDN, owner of The Dispersed Dietitian, told Healthline.
She explained that TikTokers are promoting it as a natural remedy for blood sugar regulation, gut health, and even weight management.
But does the okra water trend live up to the hype?
Okra provides numerous health benefits
Okra is packed with nutrition.
Okra is an excellent source of vitamins K and C and provides a notable amount of folate, vitamin B6, manganese, and thiamin.
Okra is also very low in calories, at just 33 calories per cup. If it’s not prepared with any added oils, it’s also fat-free.
It additionally provides 3 grams of fiber. Graham says okra contains soluble fiber, which may help slow digestion and support stable blood sugar.
According to Graham, it also contains a gel-like substance called mucilage, which may act as a prebiotic, helping to support healthy gut bacteria.
Okra is rich in polyphenols, an antioxidant that may help protect heart health by lowering blood pressure, cholesterol, and inflammation.
Does okra water have health benefits?
While okra has many health benefits, Graham said it’s unclear just how much of its nutrients actually transfer into the water.
Even though it’s nutritious as a food, those benefits won’t necessarily apply to what’s been absorbed by the water.
Graham said that because of this, she feels the health claims for okra are likely overstated.
“Eating whole okra would deliver far more fiber, nutrients, and health advantages than simply drinking water it was soaked in,” she said.
While drinking okra water may not be as effective as simply eating okra, there are still some potential benefits to be derived from this trend.
“Drinking water infused with fiber-rich vegetables may promote hydration and feelings of fullness,” said Graham, pointing to how fiber slows digestion and supports blood sugar balance.
Its ability to act as a prebiotic may also aid gut health.
Finally, it is low-cost and accessible, she said, noting that it’s low-risk to give it a try.
How to make okra water
If you’d like to try the okra water trend, Madison Reeder, a registered dietitian and director of clinical operations at ModifyHealth, said to place raw, sliced okra pods in water for 8 to 24 hours. Most versions call for around two to four pods per cup.
“During that time, some of the soluble fiber disperses into the liquid, creating a slightly viscous drink,” she said.
Reeder noted that bottled versions are also on the market, though their fiber content can vary depending on how they’re processed.
“People typically drink 8 ounces per day, often in the morning on an empty stomach,” she said, noting that the flavor is mild, earthy, and grassy with a slippery texture.
Since some may find the drink a bit off-putting, it is often advised to add lemon, lime, or honey to make it more palatable.
“It may appeal to people who already enjoy green juices or aloe-based drinks,” said Reeder.
Are there any drawbacks to drinking okra water?
Ro Huntriss, MSc, MRes, a registered dietitian and chief nutrition officer at Simple App, said that while okra has many health benefits, soaking it in water “isn’t a magic fix” and shouldn’t be relied upon to manage health conditions.
“[T]here’s little robust evidence to back the bigger health claims, and it shouldn’t replace medical advice or standard treatment for chronic conditions like diabetes,” she said.
Huntriss noted another potential con is the slimy texture, which some people might not enjoy.
Reeder said that some people may experience mild bloating or digestive changes when they increase their fiber intake too quickly.
“It’s best to start with a small amount and observe how your body responds,” she said. “Drinking it slowly, on an empty stomach, or separate from meals may help reduce discomfort.”
Reeder added that okra is high in oxalates, which she explained is a naturally occurring compound associated with kidney stone formation in those who are susceptible to them.
“This doesn’t make okra harmful for the average person,” she said, “but those with a history of kidney stones or on a low-oxalate diet should speak with a healthcare provider before making okra water a daily habit.”
Okra water has potential, but whole okra is best
Okra water is a low risk way to get more hydration, but the overall nutrient content is minimal. While it may not be the miracle tonic some TikTokers claim, it’s not without its perks.
For instance, the trend could help turn some people onto okra who might have otherwise avoided it. “It may encourage people to experiment with more whole plant foods, which is positive,” Huntriss said.
Staying hydrated and exploring new ways to engage with whole plant foods are good things — and if sipping on a cup of okra-infused water helps someone take a step toward better habits, that’s a win.
Just remember: Okra water is not a substitute for medication or a cure-all for health conditions.
The best way to enjoy the full spectrum of okra’s nutritional benefits is still the old-fashioned way — by eating it. Whether you like it grilled, roasted, or in a hearty gumbo, whole okra remains the star of the show.
So, if you’re curious, go ahead and try okra water — just remember to pair it with a balanced diet and realistic expectations.
Is Okra Water Actually Healthy? What Experts Think of the New TikTok Trend Read More »